
RFID Tags: Detailed Explanation and Practical Applications
RFID tags (Radio Frequency Identification tags) are electronic labels that use radio waves for data transmission and storage.
RFID labels are revolutionizing the way we track and manage inventory, assets, and even laundry. But what exactly are they, and how do they work? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of RFID labels, their applications, and why they’re becoming increasingly important in various industries. Whether you’re a business owner looking to streamline operations or simply curious about this technology, this article will provide valuable insights into the power and potential of RFID labels.
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification, and RFID labels are small, smart tags that use radio waves to communicate information. But let’s break it down further:An RFID label typically consists of two main components:
These components are embedded in a label or tag that can be attached to various items. The magic happens when an RFID reader sends out radio waves. The label’s antenna picks up these waves, powers up the chip, and sends back the stored information.What sets RFID labels apart from traditional barcodes is their ability to be read without direct line of sight and the capacity to store more data. This makes them incredibly versatile for tracking and managing inventory, assets, and even people in some cases.
Understanding the mechanics behind RFID labels can help you appreciate their capabilities. Here’s a simple breakdown:
This entire process happens in a fraction of a second, allowing for rapid and efficient data collection. The range at which RFID labels can be read varies depending on the type of RFID system used, from a few centimeters to several meters.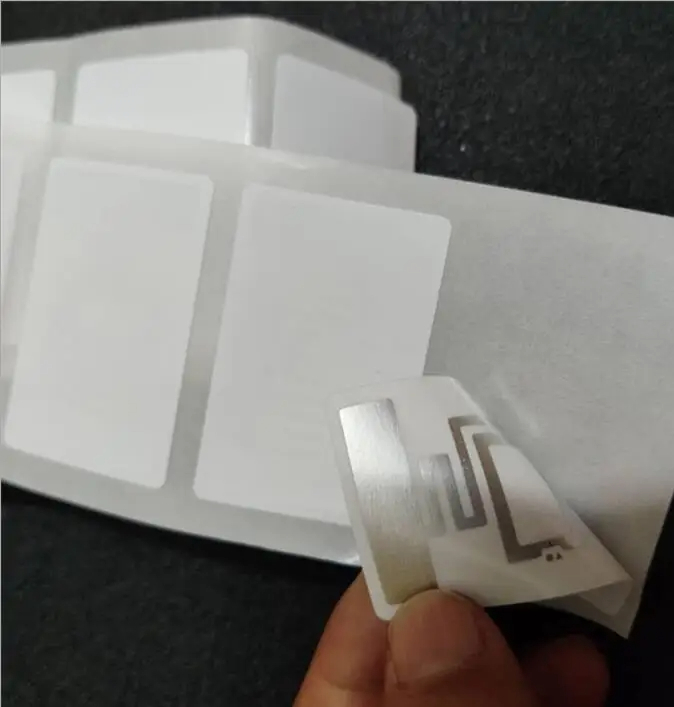
RFID labels come in various forms, each suited for different applications. Here are the main types:
Each type has its strengths, and the choice depends on factors like the application, environment, and budget.
RFID labels pack a lot of functionality into a small package. Here are some of their standout features:
These features contribute to the versatility and efficiency of RFID technology across various industries.
While both RFID labels and barcodes are used for item identification, they have some key differences:
Feature | RFID Labels | Barcodes |
Reading Method | Radio waves | Optical scan |
Line of Sight | Not required | Required |
Read Range | Up to several meters | Close proximity |
Data Capacity | Higher | Lower |
Simultaneous Reads | Multiple | Single |
Durability | More durable | Can be damaged easily |
Cost | Higher | Lower |
Data Modification | Often rewritable | Not modifiable |
While barcodes are still widely used due to their low cost, RFID labels offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency and data capacity.
RFID labels have found applications across numerous industries. Here are some popular uses:
These applications demonstrate the versatility of RFID labels in improving efficiency and accuracy across various sectors.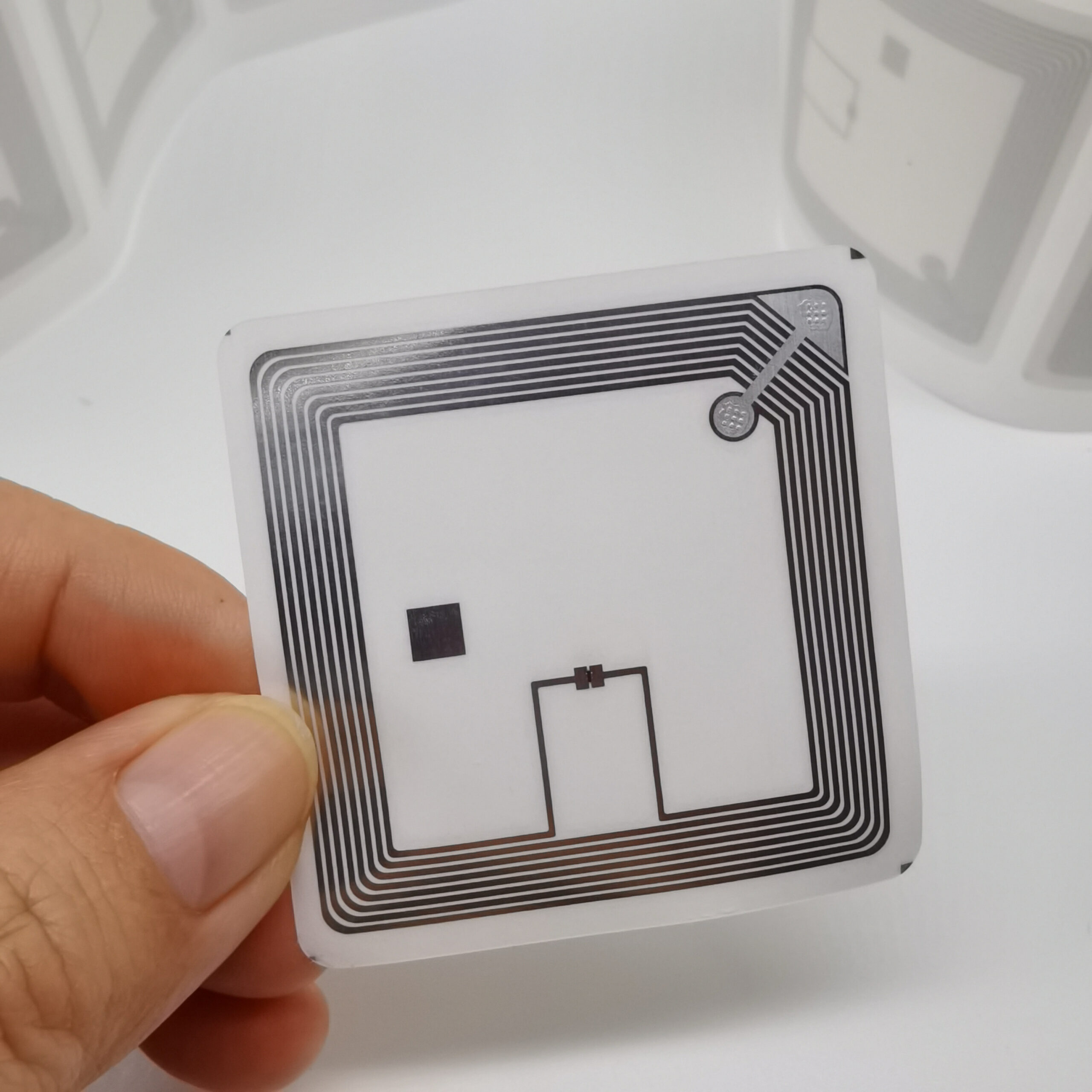
Compatibility is a crucial factor when considering RFID technology. Here’s what you need to know:
While RFID technology is becoming more standardized, it’s essential to check compatibility when setting up or expanding an RFID system.
Security is a top concern when it comes to any data-carrying technology. RFID labels offer several security features:
However, like any technology, RFID is not 100% secure. Users should implement additional security measures, especially when dealing with sensitive information.
Selecting the appropriate RFID labels is crucial for the success of your RFID implementation. Here are some factors to consider:
By carefully considering these factors, you can select RFID labels that best suit your specific needs and applications.
As we look ahead, the future of RFID label technology seems bright and full of potential. Here are some trends and possibilities to watch for:
The versatility and efficiency of RFID labels make them a technology with vast potential for innovation and application in numerous fields.In conclusion, RFID labels are a powerful tool that’s transforming the way we track, manage, and secure assets across various industries. From streamlining inventory management to enhancing supply chain visibility, these small but mighty tags are proving their worth in countless applications.Here’s a quick summary of the key points to remember about RFID labels:
As we continue to embrace the capabilities of RFID labels, we’re sure to see even more innovative applications emerge. Whether you’re looking to improve inventory management, enhance security, or streamline operations, RFID labels offer a world of possibilities to explore.
Newest trends and common knowledge in RFID laundry tags.

RFID tags (Radio Frequency Identification tags) are electronic labels that use radio waves for data transmission and storage.
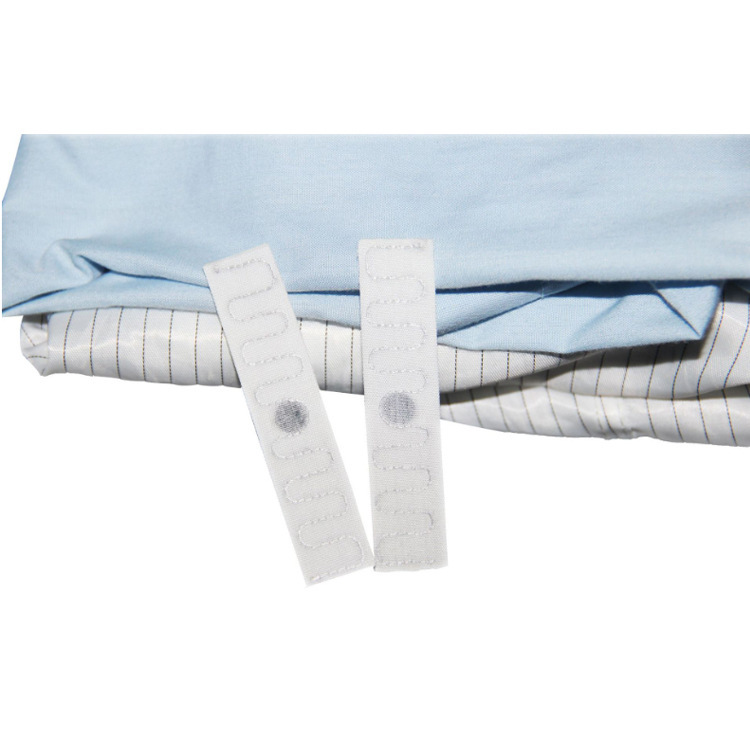

Embracing RFID laundry tags can revolutionize the way you manage linen in your laundry facility, whether it’s large-scale or smaller in size.
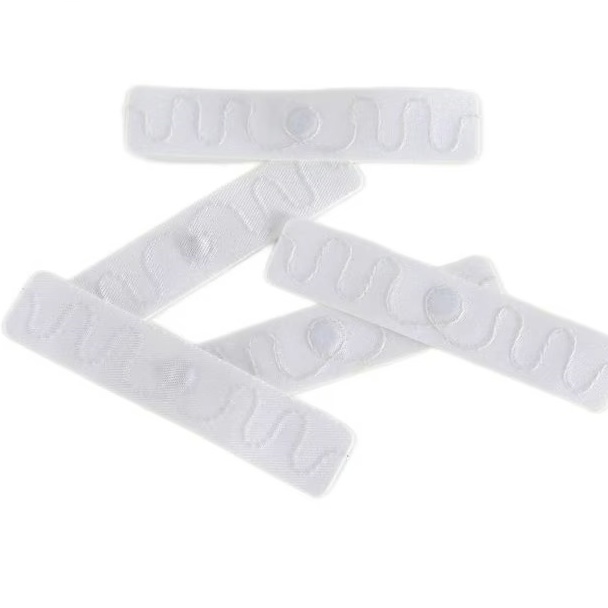

Fabric Textile UHF RFID Laundry Tags are specially designed RFID transponders tailored for textile products subjected to various industrial cleaning processes, such as sterilization, washing, and ironing.
Didn’t find what you want? Ask our manager for help!