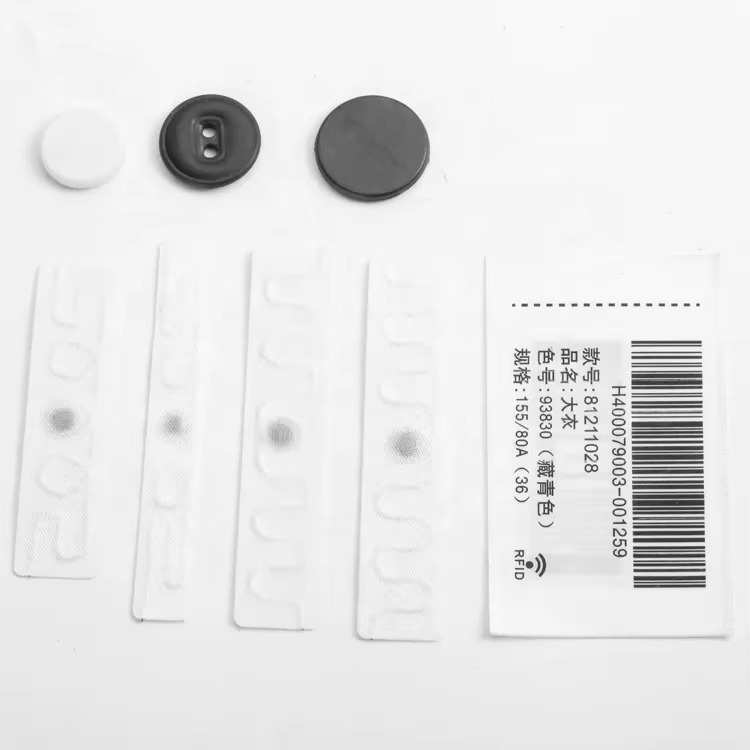

Revolutionize Your Laundry Operations with RFID Laundry Tags
Durable RFID Laundry Tags revolutionize garment tracking in industrial laundries, offering efficiency, inventory accuracy, and cost savings for seamless operations.
RFID tags (Radio Frequency Identification) have become essential in industries like logistics, retail, healthcare, and beyond. As companies focus on sustainability, many wonder: Can RFID tags be reused? The simple answer is yes, but there’s more to it.
This article will explore everything you need to know about RFID tag reusability, from how they work to the pros and cons of reusing them. Whether you’re a business owner, a supply chain manager, or just curious about the technology, you’ll find valuable insights here.
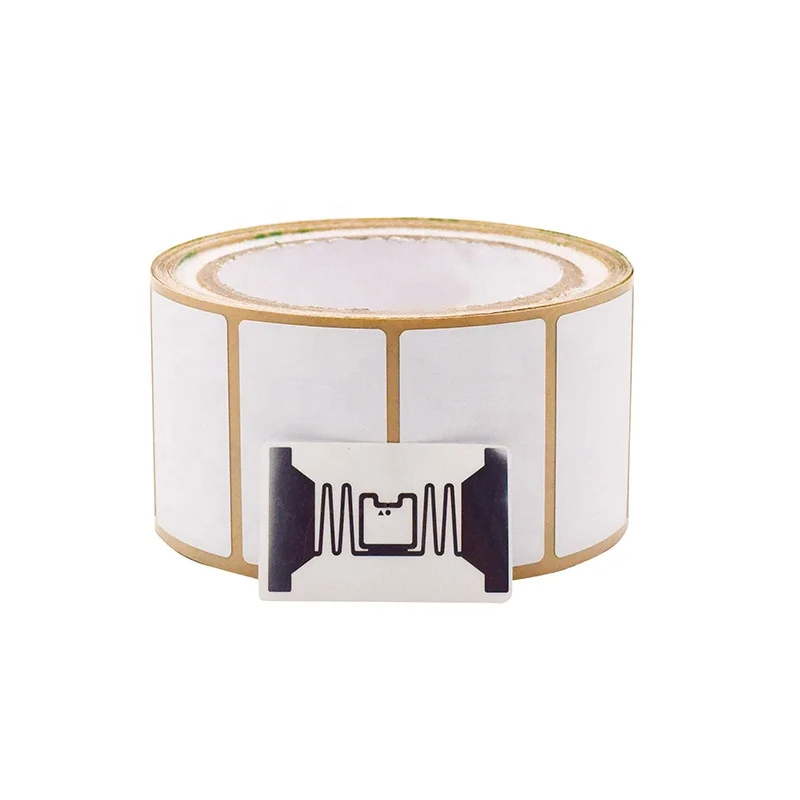

An RFID tag is a small device used to identify and track objects wirelessly using radio waves. Unlike barcodes, which require a direct line of sight, RFID tags can be read remotely by an RFID reader.
When an RFID tag comes near a reader, it transmits its stored information, enabling fast and efficient tracking. This makes RFID technology indispensable for applications like inventory management, asset tracking, and even access control in secure facilities.
RFID tags fall into two main categories: passive and active. Each serves a unique purpose, and understanding the difference is key to determining if a tag can be reused.
Passive tags rely on energy transmitted from an RFID reader to function. Since they don’t have an internal battery, they are smaller, lighter, and more affordable.
Active tags have their own power source, usually a battery, allowing them to transmit data over longer distances without needing to be near a reader.
The lifespan of an RFID tag depends on several factors, including its type, usage frequency, and environmental conditions.
| Tag Type | Lifespan | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Passive RFID | Up to 20+ years | Protected from water, metal, extreme temperatures. |
| Active RFID | A few months to several years | Battery life, frequency of data transmission. |
Passive tags generally last longer because they lack a battery, while active tags have a finite lifespan limited by their power source.
Not all RFID tags are reusable. Some tags, like WORM (Write Once, Read Many) tags, are designed to store data permanently and cannot be rewritten.
However, most read-write RFID tags can be reused multiple times, provided they are in good condition and compatible with reprogramming.

Reusing RFID tags involves a few essential steps:
Tip: Use protective casings to extend the life of reused tags, especially in harsh environments.
Reusing RFID tags offers numerous advantages, both economic and environmental.
Reusing tags reduces the need to buy new ones, lowering operational costs, especially in large-scale applications like supply chain management.
Recycling and reusing RFID tags contribute to reducing electronic waste, aligning with sustainability goals.
Reusing tags ensures a steady supply of tracking devices, minimizing downtime and improving inventory tracking systems.

While reusing RFID tags has many benefits, it’s not without challenges.
Reprogramming tags requires careful data management to avoid errors, especially when handling thousands of tags.
Tags exposed to harsh environments may degrade over time, affecting their performance.
RFID tags are versatile and can be repurposed across different industries.
As RFID technology evolves, manufacturers are focusing on developing tags that are more durable, eco-friendly, and capable of lasting longer. Future innovations may include:
An RFID tag (Radio Frequency Identification) is a small device that stores information and uses radio waves to communicate with an RFID reader. It is commonly used for tracking and identifying objects in various industries like logistics, retail, and healthcare.
Yes, many RFID tags, especially read-write tags, can be reused by erasing and reprogramming their data. However, WORM (Write Once, Read Many) tags cannot be reused as they are designed to store data permanently.
RFID tags come in two main types:
To reuse an RFID tag:
Yes, reused RFID tags can be reliable if they are in good condition and properly reprogrammed. However, tags exposed to harsh environments may degrade over time and become less reliable.
RFID tags offer a powerful solution for tracking and managing assets across industries. While not all tags can be reused, many can, providing significant cost and environmental benefits.
Investing in reusable RFID tags is a smart move for businesses looking to reduce costs and contribute to a greener future.
Newest trends and common knowledge in RFID laundry tags.

Durable RFID Laundry Tags revolutionize garment tracking in industrial laundries, offering efficiency, inventory accuracy, and cost savings for seamless operations.

In the fast-paced world of hospitality, where every detail counts towards guest satisfaction, efficient laundry management stands as a pivotal element. From plush towels to crisp bed linens, hotels and resorts strive for excellence in cleanliness and presentation.
In today’s fast-paced world, technology is continuously evolving, enhancing convenience and efficiency in our daily lives. RFID tag utilizes electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects.
Didn’t find what you want? Ask our manager for help!